- Main
- News and events
- Surgical treatment of radial bone head dislocation in dogs of dwarf breeds
Surgical treatment of radial bone head dislocation in dogs of dwarf breeds

Such dislocation in small breed dogs is the exception rather than the common phenomenon. However, such cases occur mainly due to asynchronous growth of the radial and ulnar bones. One of them is shortened, which leads to improper formation of the elbow joint. Due to the delay in treatment with a shortened ulna, the block-shaped notch is located distally and the ulnar process begins to press on the shoulder block. In dogs of dwarf breeds, this can lead to cranial dislocation of the radial bone head.
Osteotomy to lengthen the ulna
Along the edge of the ulna, located closer to the dog's tail, an incision is made: from the medial area to the hump of the ulnar process, to the middle of the diaphysis of the ulna. The subcutaneous tissues of the fascia are cut along the same line. Bilateral dissection of the capsule of the ulna opens the area of the block-shaped notch - distal to it with a special saw is performed oblique osteotomy.
Sutures are then applied to the capsule, and the fascia of the elbow flexor wrist is sutured to the elbow lateral fascia. Leather and subcutaneous tissue are sewn separately by hand.
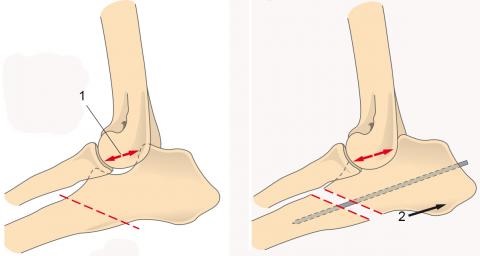
Figure 1. Osteotomy that lengthens the ulna, as well as the reduced distance between the head of the radial bone and the ulnar process
Figure 2. Proximal displacement of the ulnar process after osteotomy.
Rehabilitation period and postoperative prognosis
After the operation, a radiographic examination is required to determine the position of the bones and the condition of the elbow joint. Early mobility is important for recovery after dislocation, but the best choice is to walk on a leash without excessive activity, so that the fusion of the osteotomy is normal.
After surgical treatment in small breed dogs, the functioning of the elbow joint is normalized. However, it should be borne in mind that this problem may to some extent develop secondary osteoporosis. If a dislocation of the elbow joint occurs due to asynchronous growth of the forearm bones, the earliest surgery improves the prognosis for recovery.
